Why markets are optimistic
.
China seems to be well on its way to our 5.3 per cent growth forecast for 2023, which is slightly higher than consensus (5.1 per cent as I write this) and higher than our earlier estimate of 4.5 per cent back in 2022.
We had expected China’s COVID exit strategy to be bumpy and gradual. It turned out be even bumpier and not at all gradual after the country’s sudden reversal on its zero-COVID policy. China’s Center for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 80 per cent of the population has already been infected by COVID, so the nation may have already passed peak infection levels and achieved herd immunity, lowering the hurdles for further economic growth this year. This will likely have a positive impact not just on China but globally.
That said, recent surges in the global equity and commodity markets suggest that some may be overly optimistic about the impact China’s rebound will have on the rest of the world.
Why the impact may not meet expectations
What’s causing this rosy outlook? Drawing upon experiences in the United States and other developed countries, some media and market watchers are anticipating what they call “revenge spending”—pent-up demand and accumulated savings after three years of COVID lockdowns leading to a tide of Chinese consumer spending that will lift all boats. Some have estimated that as much as RMB 4 trillion to 6 trillion of excess savings accumulated over the past three years may flood the world’s markets.
In our opinion, the actual range is substantial but more modest. Depending on different assumptions of the saving trend, we believe that China’s excess savings over the past three years could be in the range of RMB 1.5 trillion to 4 trillion, but closer to the lower end—roughly RMB 2 trillion, or AUD 431 billion.
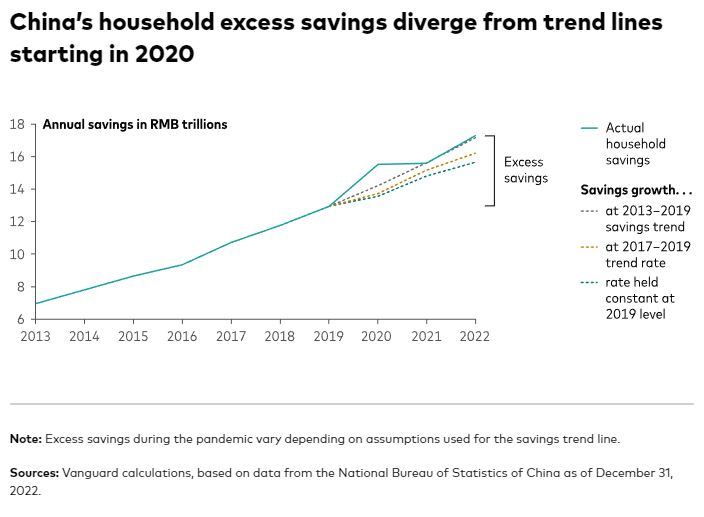
Several factors play into our more moderate estimate of the impact:
- Much of the savings over the past three years came from fewer home purchases and from redemptions of investments during a period of market turmoil—not the kind of savings that people would readily use for consumer goods and services.
- Unlike consumers in developed markets, Chinese households didn’t experience a persistent supply shortage of goods. Further, auto sales have been largely front-loaded in the second half of 2022, thanks to tax incentives. So there may be less pent-up demand than some would expect.
- Household fundamentals are also much weaker than in developed markets because of surging household debt over the past decade, limited fiscal transfer during the pandemic, three years of low income growth and high unemployment, and negative wealth effects from the sharp decline in housing prices last year.
- Most of the excess savings are held by wealthy households, who have less propensity to spend than the less affluent, at least in proportion to their assets. For the less wealthy, the precautionary saving incentive is unlikely to fade immediately given the lagging recovery in labor markets, the flimsy social safety net, and the uncertain long-term outlook.
- Chinese household consumption accounts for only 38 per cent of the country’s GDP; in comparison, in the United States, it’s roughly 70 per cent of GDP. Increasing China’s private consumption by 10 per cent translates to a 4 per cent increase in its GDP. So the impact will not be as great for China as it was for the U.S. when it went through its post-lockdown bounce.
Who would benefit the most from Chinese consumers
Any immediate rebound in consumption could come from the well-off in China more than the common laborer. When the affluent do spend, the immediate beneficiaries will likely be the makers of luxury goods, the tourism industry, and educational services.
In pre-COVID 2019, Chinese travelers accounted for roughly 20 per cent of all tourism spending, according to data from the World Trade Organisation. If that type of spending pattern resumes for 2023, the economies most likely to benefit are those in Asia. (Nine of the top 10 countries most visited by Chinese tourists in 2019 were in Asia).
Educational services—primarily overseas study at universities—will also likely rebound, mainly in Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
A rebound in China’s economy, particularly for travel, will also benefit exporters of commodities such as oil and natural gas. However, this also means higher inflationary pressures that present a challenge for central banks.
Why we might just avoid a global recession
China already accounts for about 20 per cent of the global economy. Any rebound in its demand for imported goods and services will have a positive impact, if not necessarily of the magnitude others might expect.
Last year, we estimated that the likelihood of a global recession in 2023 was roughly 50/50. With China rebounding at our projected rate, we believe that chance is now less than 50 per cent. (The World Bank defines a global recession as an annual contraction in world real per capita GDP accompanied by a broad decline in various other measures of global economic activity.)
Why our outlook for China’s long-term growth is guarded
Despite the cyclical upturn, our long-term outlook for China is cautious. As we pointed out in our 2021 paper, China has several structural challenges—among them, an aging population, fading globalisation, and a retreating private sector—and that hasn’t changed. China’s population fell in 2022 for the first time since 1961. China might grow old before it becomes rich.
Over the long run, China’s annual GDP growth may fall to the 3 per cent‒4 per cent range or lower—still healthy and more sustainable, but not quite the economic engine that has helped boost the global economy in recent decades.
For now, China may provide just enough impetus to keep the world economy from dipping into a recession.
Qian Wang
Chief Economist, Asia-Pacific
Head of the Vanguard Capital Markets Model
vanguard.com.au
